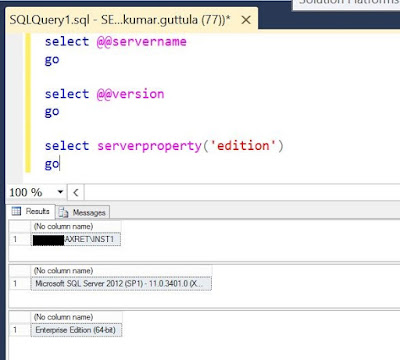
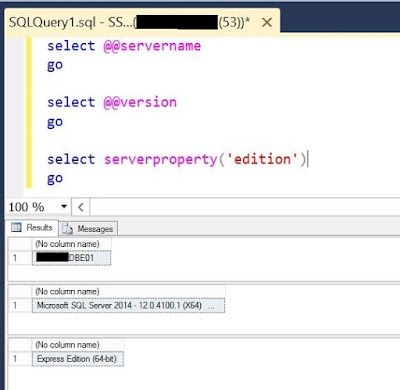
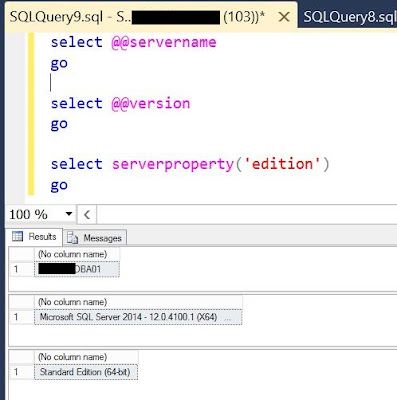
In this post, the focus will be on some basic setup which needs to be understood and implemented for having a functional AX Retail.
Assuming that you have already installed the necessary AX Retail components beforehand. If not, Please go through the below links, which you can find already on Internet (no need for any Partner permissions)
So now let's focus on what all steps you have to take, settings which you have to configure at the AX Retail HeadQuater level in order to have a functional AX Retail. Kindly note that I am us
Configure and Validate Retail Headquarter settings:
After the successful installation of components, it is very important to initialize a set of jobs.
* Retail channel schemas
* Scheduler jobs
* Distribution schedule
Generate classes - will create the necessary methods in the RetailCDX* classes for download/upload of the data between AOS and Async server.
2. Verify Store:
For a retail setup, the next most important to check is the Stores. Few configurations and setup which I feel are important are as below
Path: Retail > Common > Retail channels > Retail Stores.
Choose (double click on) the store on which you would like to work and verify the setup, say MIAMI for example (in Contoso data)
3. Publish Channels:
This step is necessary to make the store Active and involves very simple process.
Path: Retail > Common > Retail channels > Retail Stores.
Click Publish on the Ribbon > Setup. And click Yes on the Message box that pops up.
4. Retail Store Management and Security:
This is basically to view and enable the necessary Store workers the access to work on POS devices. Involves a set of simple steps.
5. Hardware profiles:
Hardware profile is used to set preferences and properties for a register and peripherals of the register, such as the cash drawer and the receipt printer.
Path: Select Store (MIAMI) > Registers (Factbox). Click on Hardware profile (In General fasttab > Profiles)
And setup necessary Hardware profiles.
6. Configuring CDX:
Configuring the Commerce Data Exchange consists of several steps again:
1. Message Database configuration:
This has to be performed in AX Form, Path: Retail > Setup > Parameters > Retail scheduler parameters.
Make sure the "Server name" points to the AsyncServer name and
"Database name" points to the AsyncServer Database.
2. Aysnc Server profile:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Async Server profile.
Verify that profile exists. The Data download and Upload intervals provide the time intervals for request and response. Type '0' for an immediate response.
3. Working folders:
The working folders are needed for the temporary placement of Outgoing and Incoming data. Can be setup in AX form, Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Working folders.
Verify that the records exist for both Download and Upload paths. Also validate the permissions for folders - both AOSServiceAccount and AsyncServerServiceAccount should have read/write permissions to the selected folders.
4. Channel Data Groups:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Channel Data Group. Verify and create (if necessary) a new Channel Data group with a Unique "Name". And "Retail Channel schema" and "Working folders" should be selected from the drop-down.
Also for every Channel Data group, we would have to create Distribution schedule. Path: Retail > Periodic > Data distribution > Distribution schedule.
Add the newly created Channel Distribution Group to "Distribution schedule" and create batch jobs accordingly.
5. Channel Database:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Channel database.
The form allows us to configure which Channels should be made available in which Database. Note: In Contoso Demo data, every Single store is mapped to Single channel Database.
Create a new Channel Database ID (unique) by filling the necessary fields. 'Username/Password' combination should match values used during installation of Async client instance for the corresponding Channel Database.
'Retail Server' FastTab information purpose is to be able to have active database assignments for each channel.
6. Real-time service profiles:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Real-time Service profiles.
Create a new records, fill in necessary fields under table 'Retail time service location', Server (certificate name), Web application name (is the one used during installation).
The checkbox under FastTab:Settings, set true, if User login credentials for Realtime POS or modern POS should always query real time service for validation.
7. Verifying Retail Server configuration:
The validation can be done from Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Channel profiles.
Validate all the fields as per settings done above. And 'Retail server URL' is the one which Modern POS users. 'Media based URL' is the one where the Images in Retail POS are hosted. 'Hardware station URL' is to connect with the peripherals like printer/barcode scanners.
Certificate Management:
Before Aysnc server is installed, the SSL certification should be configured. This is to ensure secure communication between Async server and Aysnc client.
Go to Path: IIS > Select Server > Server certificates > Create new Self-signed certificate. Provide necessary details.
The code to be provided during installation can be found on the newly created certificate. Go to Path: Double-click on the certificate > Details > Thumbprint. Copy the code.
Async Server:
Another setup to be performed on the Async server level is to, Go to Path: Retail > Setup > parameters > Retail scheduler parameters > Click button "Sync Metadata".
Thanks for reading, hope it helps. Will update more details as I dig more into the setup. Happy DAXing.
Assuming that you have already installed the necessary AX Retail components beforehand. If not, Please go through the below links, which you can find already on Internet (no need for any Partner permissions)
- A nice Youtube video explaining Retail Topology - See here
- Also you can find the Microsoft's Retail Deployment Guide - PDF here
So now let's focus on what all steps you have to take, settings which you have to configure at the AX Retail HeadQuater level in order to have a functional AX Retail. Kindly note that I am us
Configure and Validate Retail Headquarter settings:
- Initialize Base configuration for AX Retail
- Verify Stores
- Publish channels
- Retail store management and security
- Hardware profiles
- Configure Commerce Data Exchange (CDX)
- Verify Retail server configuration
- Check Infolog's generated for more information
- Restart AOS
After the successful installation of components, it is very important to initialize a set of jobs.
- Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Parameters > Retail parameters.
- Click Initialize button.
- This will popup a Message box: "Initialize the base configuration data for Retail"
- Click Yes
- Will take couple of minutes
- And will pop up an infolog on completion.
- Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Retail channel schema
- Click Generate classes.
* Retail channel schemas
* Scheduler jobs
* Distribution schedule
Generate classes - will create the necessary methods in the RetailCDX* classes for download/upload of the data between AOS and Async server.
2. Verify Store:
For a retail setup, the next most important to check is the Stores. Few configurations and setup which I feel are important are as below
Path: Retail > Common > Retail channels > Retail Stores.
Choose (double click on) the store on which you would like to work and verify the setup, say MIAMI for example (in Contoso data)
- Verify "Screen Layout" (Fast tab)
Validate and create new records to select for "Enterprise POS" and/or "Modern POS" based on your requirement. - Verify that at least one POS Register exists under "Registers" Factbox
- Verify that the store is assigned to the correct "Legal entity" (In General Tab > Identification)
- Verify that "Employee address book" (In General Tab > Address book) are setup correctly
- Verify that "Real-time Service profile" (In General Tab > Profiles) is setup.
3. Publish Channels:
This step is necessary to make the store Active and involves very simple process.
Path: Retail > Common > Retail channels > Retail Stores.
Click Publish on the Ribbon > Setup. And click Yes on the Message box that pops up.
4. Retail Store Management and Security:
This is basically to view and enable the necessary Store workers the access to work on POS devices. Involves a set of simple steps.
- On the Retail store, in our example, MIAMI. Click Workers on the Ribbon > Set up.
- AX directs to the list of all the Workers on this store. Validate and "Hire New Worker" if needed.
- Double click on the worker and validate that the Worker should have the correct address (Profile Tab > Worker summary > Other information > Address books)
- Go to Retail Tab
- Click on Hyperlink "POS Permissions" (Under Retail > Information)
- Validate the permissions and "Override permissions" if necessary
- Verify "manageDevice" is checked in order to have the Worker be able to work on the POS
5. Hardware profiles:
Hardware profile is used to set preferences and properties for a register and peripherals of the register, such as the cash drawer and the receipt printer.
Path: Select Store (MIAMI) > Registers (Factbox). Click on Hardware profile (In General fasttab > Profiles)
And setup necessary Hardware profiles.
6. Configuring CDX:
Configuring the Commerce Data Exchange consists of several steps again:
1. Message Database configuration:
This has to be performed in AX Form, Path: Retail > Setup > Parameters > Retail scheduler parameters.
Make sure the "Server name" points to the AsyncServer name and
"Database name" points to the AsyncServer Database.
2. Aysnc Server profile:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Async Server profile.
Verify that profile exists. The Data download and Upload intervals provide the time intervals for request and response. Type '0' for an immediate response.
3. Working folders:
The working folders are needed for the temporary placement of Outgoing and Incoming data. Can be setup in AX form, Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Working folders.
Verify that the records exist for both Download and Upload paths. Also validate the permissions for folders - both AOSServiceAccount and AsyncServerServiceAccount should have read/write permissions to the selected folders.
4. Channel Data Groups:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Channel Data Group. Verify and create (if necessary) a new Channel Data group with a Unique "Name". And "Retail Channel schema" and "Working folders" should be selected from the drop-down.
Also for every Channel Data group, we would have to create Distribution schedule. Path: Retail > Periodic > Data distribution > Distribution schedule.
Add the newly created Channel Distribution Group to "Distribution schedule" and create batch jobs accordingly.
5. Channel Database:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Channel database.
The form allows us to configure which Channels should be made available in which Database. Note: In Contoso Demo data, every Single store is mapped to Single channel Database.
Create a new Channel Database ID (unique) by filling the necessary fields. 'Username/Password' combination should match values used during installation of Async client instance for the corresponding Channel Database.
'Retail Server' FastTab information purpose is to be able to have active database assignments for each channel.
6. Real-time service profiles:
Go to Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Real-time Service profiles.
Create a new records, fill in necessary fields under table 'Retail time service location', Server (certificate name), Web application name (is the one used during installation).
The checkbox under FastTab:Settings, set true, if User login credentials for Realtime POS or modern POS should always query real time service for validation.
7. Verifying Retail Server configuration:
The validation can be done from Path: Retail > Setup > Retail scheduler > Channel Integration > Channel profiles.
Validate all the fields as per settings done above. And 'Retail server URL' is the one which Modern POS users. 'Media based URL' is the one where the Images in Retail POS are hosted. 'Hardware station URL' is to connect with the peripherals like printer/barcode scanners.
Certificate Management:
Before Aysnc server is installed, the SSL certification should be configured. This is to ensure secure communication between Async server and Aysnc client.
Go to Path: IIS > Select Server > Server certificates > Create new Self-signed certificate. Provide necessary details.
The code to be provided during installation can be found on the newly created certificate. Go to Path: Double-click on the certificate > Details > Thumbprint. Copy the code.
Async Server:
Another setup to be performed on the Async server level is to, Go to Path: Retail > Setup > parameters > Retail scheduler parameters > Click button "Sync Metadata".
Thanks for reading, hope it helps. Will update more details as I dig more into the setup. Happy DAXing.